What is the thyroid gland and what does it do?
Early warning signs of thyroid problems:
- Overactive thyroid: Racing heart rate and palpitations, anxiety, insomnia, nervousness, unintended weight loss with increased appetite, excessive sweating/heat intolerance, and muscle weakness.
- Underactive thyroid: Fatigue/sluggishness (mental and physical), cold intolerance, constipation, hair loss, weight gain, and depression.
What are the physical signs of thyroid nodules/cancer:
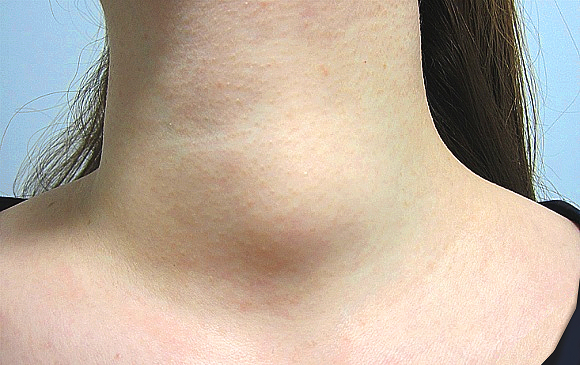
- An unusual lump or swelling in the neck
- A new cough
- Hoarseness in the voice
- Trouble swallowing
- New persistent cough
- Trouble breathing
Within the year, thyroid cancer went from #2 in young adults to it being the #1 cancer in that age group.”
– Melanie Goldfarb, MD
What you need to know about thyroid health: Tips from the Expert
Dr. Melanie Goldfarb stands outside Saint John’s Health Center discussing thyroid cancer with Saint John’s Cancer Institute
Thyroid Cancer Facts:
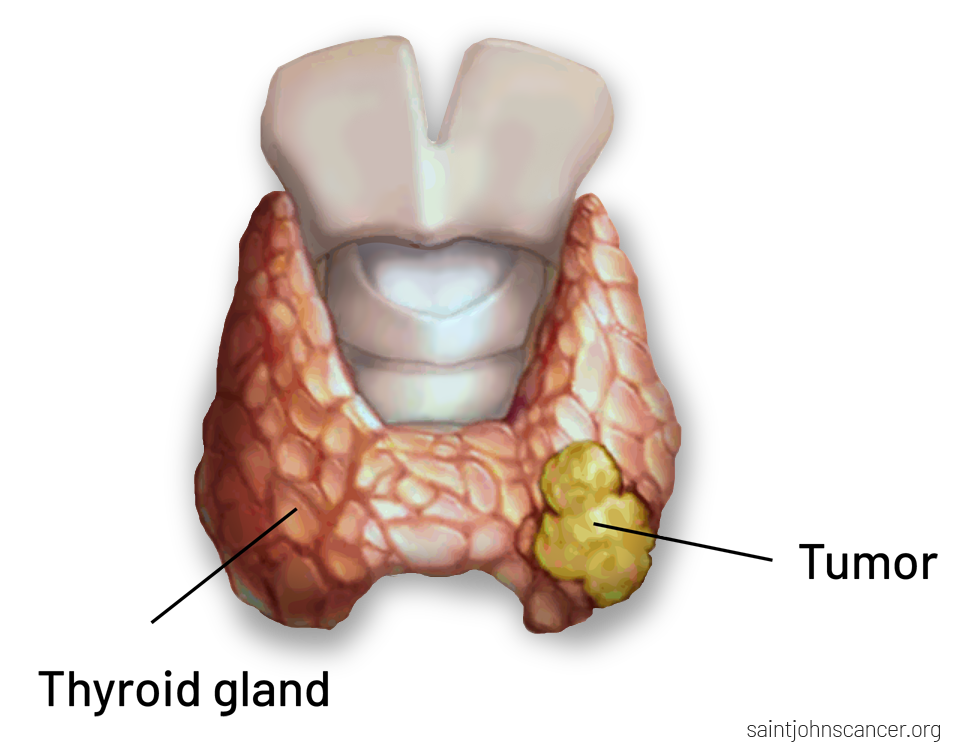
- Most thyroid cancers are slow-growing.
- Thyroid cancer is more common in women than men.
- Women from the ages of 15 to 39 are being diagnosed more frequently with thyroid cancers.
- The 5-year survival rate for localized thyroid cancer is 99.9 percent.
- 3 percent of all thyroid cancers metastasize (move beyond the primary site and into other parts of the body).
Types of Thyroid Cancers:
- Differentiated (including papillary, follicular, and Hürthle cell)
- Medullary
- Anaplastic (an aggressive cancer)
Thyroid cancer is usually asymptomatic (having no physical symptoms), and in younger patients, it is usually detected when the nodule is large enough to be felt by the patient or a clinician during a physical exam. In older patients and some younger patients, it is found incidentally when imaging is performed for unrelated reasons.
Risks Factors of Thyroid Cancer include:
- Being female
- Age
- Hereditary conditions
- Family history
- Radiation exposure
- Being overweight or obese
- Lack of iodine in the diet
Most people with thyroid cancer have no known risk factors, and thyroid cancer can recur once it’s been treated.
All thyroid nodules should be evaluated with a thyroid ultrasound, and a biopsy should be taken in order to get a diagnosis. Surgery is the main form of treatment for thyroid cancer.
– Melanie Goldfarb, MD
Treatment of Thyroid Cancer:
- Active surveillance (regular ultrasound examinations)
- Surgery (See Thyroid Cancer Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Radiation therapy, radioactive iodine (adjuvant therapy)
- Thyroid hormone therapy
- Targeted Therapy
Most thyroid cancers respond well to treatment, but a small percentage can be very aggressive.
Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules can be benign (non-cancerous), and cause difficulty eating, breathing, swallowing, and become unsightly, resulting in a visible bulge in the neck. These nodules can be treated non-invasively with Radiofrequency Ablation, more commonly referred to as RFA treatment. RFA is a newer outpatient procedure for thyroid nodules that has a high success rate. It works by shrinking the nodule internally using heat generated by radio waves, which stops the growth and causes the nodule to shrink over time.
- Learn more about RFA (See Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation).
- Listen to a testimonial of an RFA treated patient, click here.
What should you know from reading this blog?
- What the thyroid is and how it regulates your body’s hormones.
- Early signs of thyroid problems.
- Signs of thyroid cancer.
- Risks of thyroid cancer.
- Treatment of thyroid cancer.
- Types of thyroid cancers.
- Treatment of benign thyroid cancer.
- Dr. Melanie Goldfarb is a dog lover.
If you believe you are experiencing any signs, or symptoms, or think you are at risk, please discuss this with your endocrinologist or contact the endocrine center of excellence and speak with Dr. Goldfarb, 310-829-8751 or click here to schedule an appointment.


