A woman’s risk of getting ovarian cancer during her lifetime is about 1 in 78, according to the American Cancer Society. This cancer mainly develops in older women.
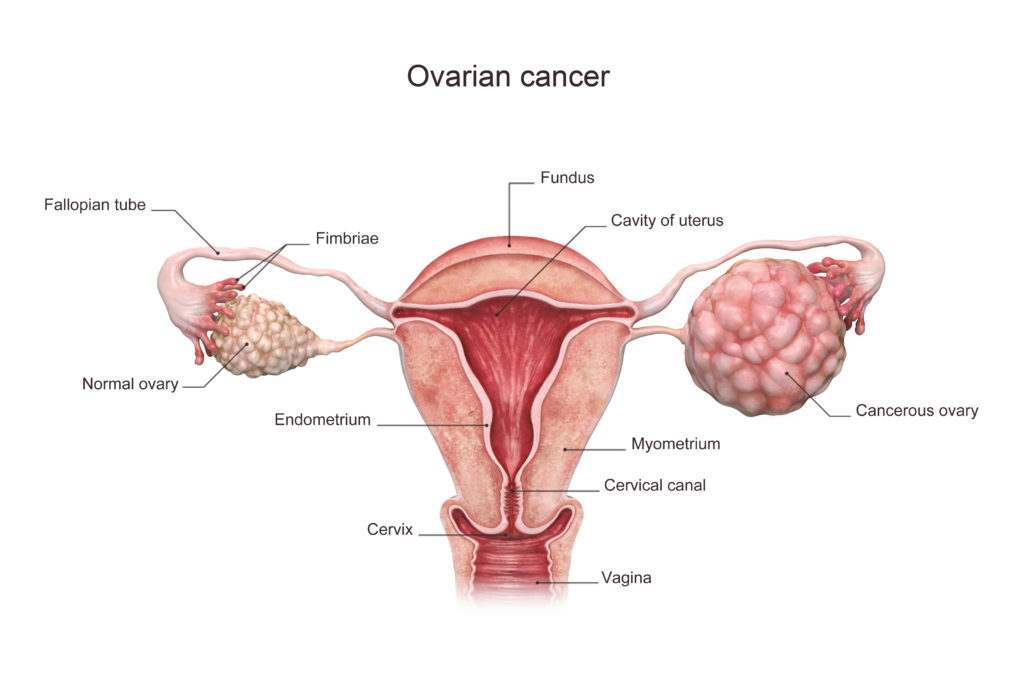
Ovarian Cancer begins in the woman’s ovaries. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones including estrogen and progesterone. Our team at the john Wayne Cancer Institute understands that personalized care is top of the list when we diagnose and treat ovarian cancer.
Causes of Ovarian cancer
- Eight out of ten ovarian cancers occur sporadically, meaning it is not inherited.
- 20% is related to a genetic mutation, like BRCA, which can be tested for if you have a strong family history.
In both cases, prevention combines mainstream medical options like oral contraceptives as well as integrative lifestyle choices including exercise, nutrition, and toxin avoidance.

Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is most often detected in later stages by biopsy of tissue or fluid. A pelvic exam, CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis, as well as a CA 125 blood test are ways to help in diagnosing ovarian cancer.