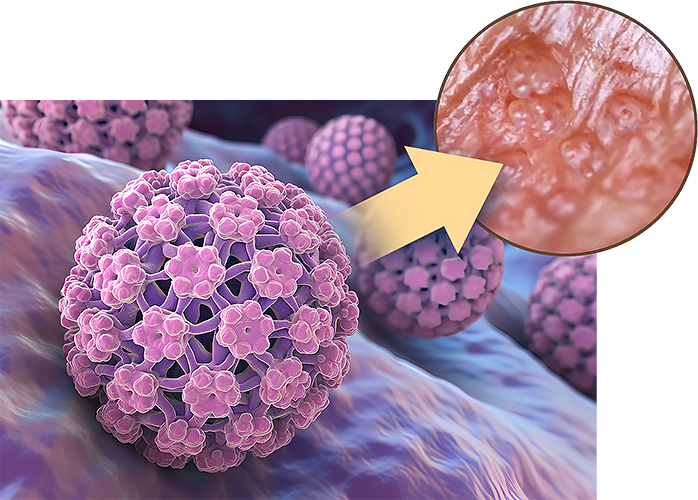
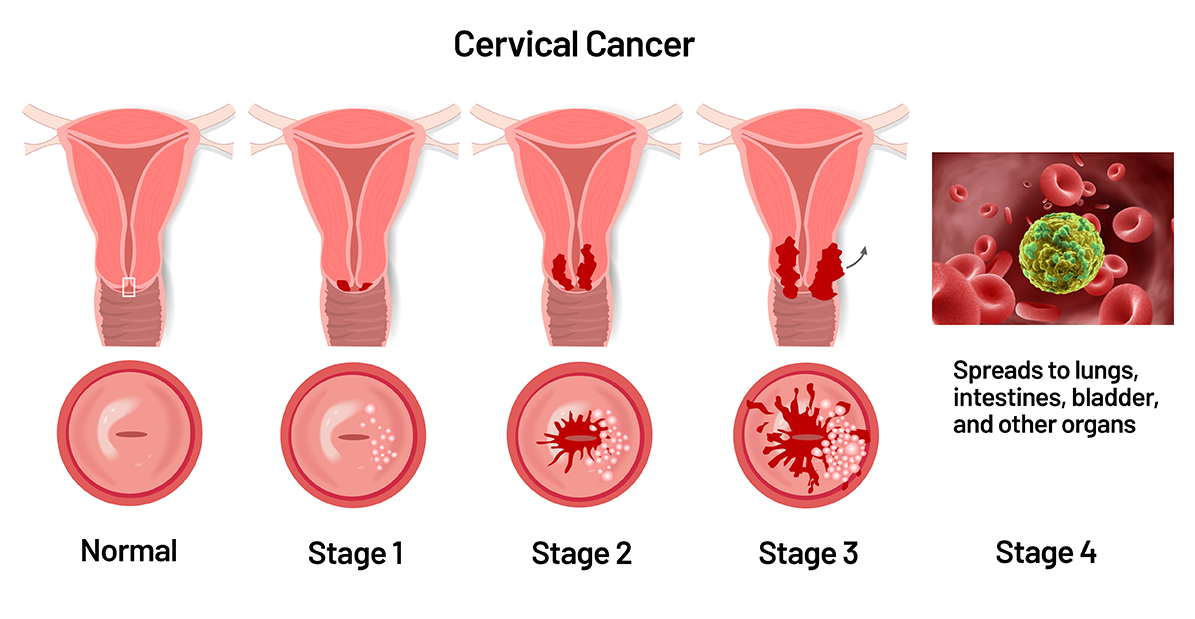
If you have questions regarding cervical cancer or would like an expert second opinion, please call today or click here to schedule an appointment.
Cervical Cancer: Causes, Signs & Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Cervical Cancer: Causes, Signs & Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Schedule An Appointment
Saint John's: A Legacy of Care Excellence - 30 Major Healthcare Awards for 2023 and 2024 including America's 50 Best for Surgical Care, Maternity, and Uterine Cancer Surgery