Why Men Should See a Urologist?
The importance of routine checkups
To all the men out there and the women who care about them, this one’s for you! As men age, their physical health needs to be looked after to screen for any issues and prevent things from getting overlooked. The prostate changes over time, as well as urinary and sexual function. It’s important to find a urologist you like and trust so you can begin to build a relationship. Starting around age 40, you should visit a urologist and make sure you continue with yearly checkups and screenings to keep you healthy.
What Does a Urologist Do?
First, a urologists aims to resolve issues concerning the urinary tract, bladder, and kidneys, in men and women. Specifically, in men, urologists are experts in the function of male organs including the penis, testes, scrotum, and prostate. It is important for all men to see a urologist as they get older because health problems can happen to with age.
Since urology is a surgical specialty, urologists can provide you with a wealth of information on a variety of health topics. Urologists encounter a wide range of health issues in their patients so please ask them about anything concerning you health-wise and they will help decide the best treatment for you.
Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatments
- Urologists offer both non-invasive and surgical treatment options, depending on your condition.
- Treatment plans may include medication, lifestyle modifications, or advanced surgical techniques.
Common Urology Problems in Men
Prostate and Testicular Cancer
Men who have a family history of prostate cancer, testicular cancer, kidney cancer, and other urologic conditions should start seeing a urologist around the age of 40. Your physician will do a complete medical history and screening exam to determine if you are at risk. Be sure to check with your insurance to see if you need a referral from your primary care doctor before seeing a urologist.
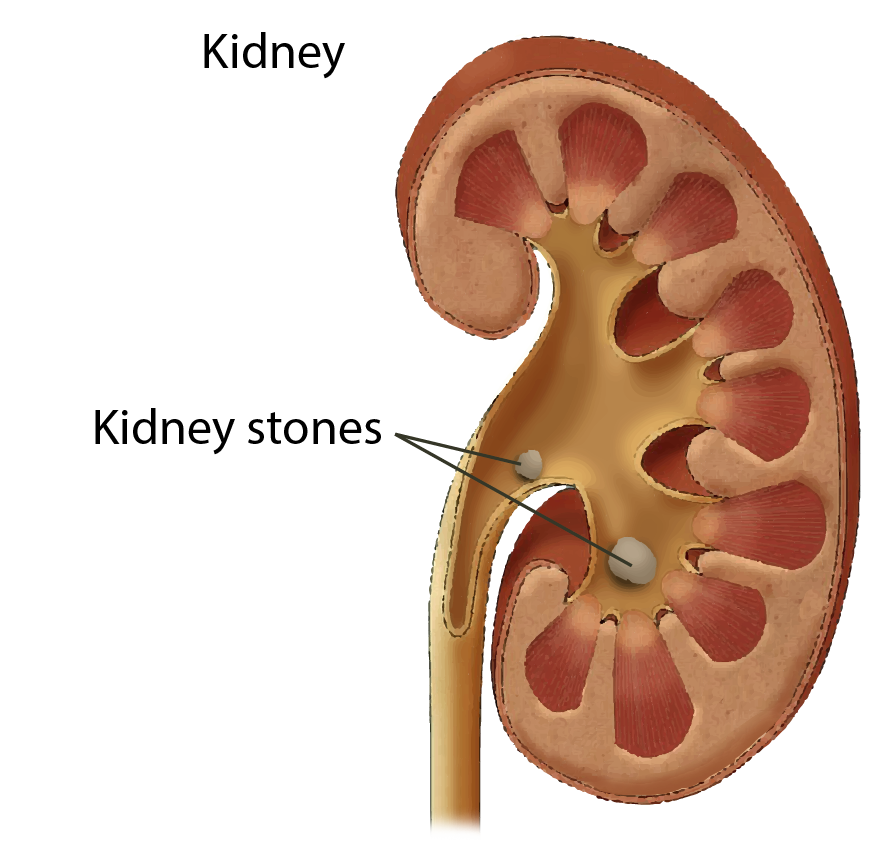
Kidney Stones and Urinary Tract Problems
- Kidney stones form from crystalized minerals in the urine.
- Symptoms include pain in the back or while urinating, nausea, or visible blood in urine.
- Risk factors include dehydration, urinary tract infections, and family history.
Screening for Urology Problems
- Prostate cancer screenings are important so a physician can check for abnormalities of the prostate. While prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men, it can often be treated successfully. Signs and symptoms include trouble urinating or the urge to go often, blood in the urine, or trouble getting an erection.
- Testicular cancer screenings are important so that a physician can check for abnormalities such as growths or lumps on the testicles. Other signs and symptoms of testicular cancer include those who have gone through early puberty, have lower back pain or breast growth or soreness.
- Urine and Blood Tests: These are often the first steps in diagnosing urologic conditions. They can detect infections, kidney function, and other abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: These include:
- Ultrasound: Used to visualize the kidneys, bladder, and prostate.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the urinary tract.
- MRI: Offers high-resolution images of soft tissues.
- Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP): An X-ray exam that uses a contrast dye to highlight the urinary tract.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder to look for abnormalities.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures the level of PSA in the blood, which can be an indicator of prostate cancer.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A physical exam where a doctor feels the prostate through the rectum to check for abnormalities.
- Urodynamic Tests: Assess how well the bladder and urethra store and release urine.
Common Urologic Tests
These methods help doctors identify conditions like urinary tract infections, kidney stones, prostate issues, and bladder problems. Regular screening is important for early detection and effective treatment.
Urology Symptoms Men Should Never Ignore
Warning Signs That Warrant a Urologist Visit
- Testicular mass
- Unusual urine odor
- Blood in the urine
- Erectile dysfunction
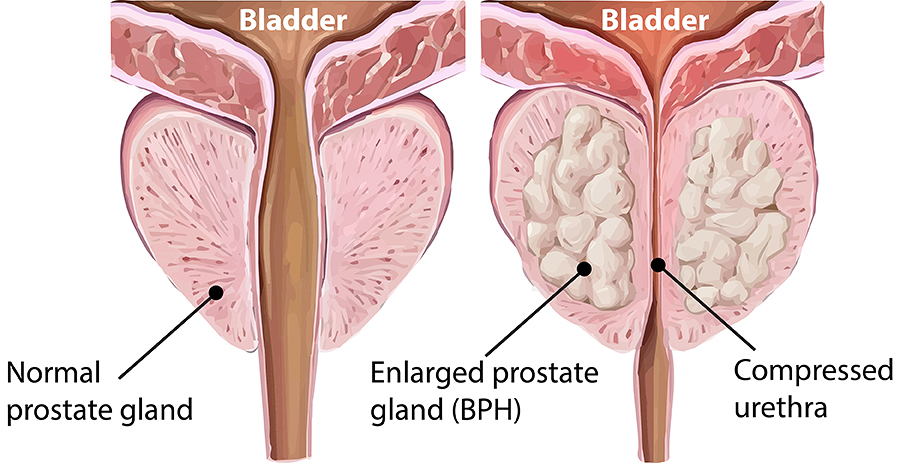
- BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia), or enlarged prostate
- Persistent pain, urinary tract discomfort, and sexual health changes may signal deeper problems.
Urologic Treatments Using Advanced Technology:
As technology continues to change and advance, we are able to provide you with the most advanced, cutting-edge treatments. If it is determined that you will need surgery, be sure to discuss with your doctor which procedure is best for you.
Focal One for Prostate
Focal One is the world’s most advanced high-intensity focused ultrasound. If you are diagnosed with localized prostate cancer, your physician may recommend Focal One which can destroy the tumor with high-intensity ultrasound waves. With this advanced procedure, we can treat your prostate cancer with less damage to surrounding healthy tissue and with fewer side effects.
Innovative Options for Eretile Dysfynction
In addition to oral medications and injections, at Saint John’s Cancer Institute we are studying new treatments for erectile dysfunction. Penile stem cell injections and shockwave therapy are being studied as additional treatment options.
Robotic Surgery for Urinary Obstruction
Surgeries for urinary obstructions are now being performed robotically. A scope is put through small incisions in the abdomen while surgical equipment is inserted through other incisions. Your physician will use a robotic consult to use the surgical equipment during the procedure.
Bladder Cancer Surgery with da Vinci Robotic System
If you are diagnosed with bladder cancer, Saint John’s Cancer Institute uses the da Vinci Surgical System. A console is used to control miniature surgical equipment to provide you with a minimally invasive surgery which leads to a faster recovery.
Visit our urology treatment pages, to find more information on different types of treatments for all urological conditions and diseases, please visit the following link.
Men, Don’t Ignore These Urology Symptoms
Signs You Should See a Urologist Right Away
- A lump or mass in the testicles
- Strong or unusual-smelling urine
- Blood in your urine (hematuria)
- Trouble getting or maintaining an erection
- Signs of an enlarged prostate (BPH), such as frequent or weak urination
Even if symptoms seem manageable, they can signal problems like infection, kidney stones, or early signs of cancer. A urologist can provide the right diagnosis and treatment plan. (added keywords: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment, problems, health)
Contact Our Urologists:
Personalized Diagnosis and Treatment Plans
Saint John’s Cancer Institute in Santa Monica, CA strives to provide all patients with personalized comprehensive care using the most advanced treatments and cutting-edge technology to the whole patient. Please contact us if you have any questions or concerns and schedule an appointment with one of our urologists. You can fill out a form and submit an online appointment request or call 310-582-7137. You can also discuss if a virtual doctor visit would be the right decision for you.
Learn More:
- Urology and Urologic Oncology Center of Excellence at Saint John’s Health Center
- Urologic Conditions and Treatments
References/Resources:
https://www.urologyhealth.org/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases