At Saint John’s Health Center, a community hospital located in Santa Monica, CA, breast evaluation is a crucial component of women’s healthcare services. The Margie Petersen Breast Center at Saint John’s exemplifies this commitment by offering comprehensive evaluation and screening services alongside its renowned breast oncologic care and research efforts.
How we evaluate breast conditions with screening and imaging
The Margie Petersen Breast Center’s focus on breast health underscores the importance of early detection and prevention in combating breast cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women. The breast center, led by Dr. Janie Grumley, Director, Comprehensive Breast Program, is known for being able to evaluate any breast condition in one day.
Breast Screening
Breast cancer screening is crucial because it helps detect cancer early, when it is most treatable. Early detection through screening can significantly reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer. The primary screening method is a mammogram, an x-ray of the breast that can identify cancer before it is large enough to cause symptoms. Women at average risk for breast cancer are generally advised to start annual mammograms between ages 40 and 44, continue yearly screenings from ages 45 to 54, and then switch to biennial screenings from age 55 onwards. For those at higher risk, additional methods like breast MRI may be recommended.
The Margie Petersen Breast Center at Providence Saint John’s Health Center offers a comprehensive and compassionate approach to breast care. We emphasize patient dignity and comfort, providing imediate access to a multidisciplinary team to address both physical and emotional needs. Services include advanced imaging, genetic counseling, nutritional support, and wellness programs like yoga and meditation. This holistic approach ensures that our patients receive personalized care tailored to their unique circumstances, enhancing both treatment outcomes and overall quality of life
Breast Examination
Breast examination is a fundamental component of breast evaluation. Performed by a healthcare provider, a breast examination is different than a self-exam. A physical exam involves palpating the breasts and underarms to detect any abnormalities such as lumps, thickening, or changes in texture. It is a simple yet effective method for identifying potential issues that may require further investigation. During the exam, your provider will physically check both of your breasts.
Learn more about breast exams including self-breast examination.
Breast Ultrasound
Breast ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique used to supplement mammography. It utilizes sound waves to create detailed images of the breast tissue, aiding in the detection and characterization of breast abnormalities. Ultrasound is particularly useful for distinguishing between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts, helping to guide further diagnostic and treatment decisions. We may recommend an ultrasound to help determine whether a breast abnormality is likely to be a fluid-filled cyst or a solid mass, which may be either benign or cancerous.
Learn more about Breast Ultrasound.
Breast Biopsy
Biopsy is a procedure performed to obtain a tissue sample from the breast for examination under a microscope. It is the most definitive way to diagnose breast cancer and determine its characteristics, such as hormone receptor status. There are different biopsy techniques, including needle biopsy and surgical biopsy, depending on the size and location of the abnormality.
Learn more about Breast Biopsy.
Breast MRI
Breast MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a supplemental imaging modality used in certain cases to provide more detailed information about breast tissue. It is often used in conjunction with mammography for high-risk individuals or to further evaluate abnormalities detected on mammograms or ultrasound.
Learn more about Breast MRI.
Mammography/Mammograms
Mammography is the primary screening tool for breast cancer, involving low-dose X-rays to detect early signs of cancer before symptoms develop. It can detect small tumors that may not be palpable during a physical exam. Regular mammograms are recommended for women starting at age 40, or earlier for those with a family history of breast cancer or other risk factors. A mammogram is considered the standard of care to screen for breast cancer.
Learn more about Mammograms.
Other Types of Diagnostic Testing
Other tests and procedures may be used depending on your situation. PET Scans (Positron Emission Tomography), for example, are not used to screen for breast cancer due to the limited ability to detect small tumors, they are useful in staging breast cancer. This includes evaluation of the lymph nodes and cancer spread to other parts of the body. Similarly, CT scans (Computerized Tomography) are not routinely used to evaluate the breasts but may be used to verify if a tumor has spread into the chest wall. This knowledge helps to determine the type of recommended surgery. Thermography or Thermal Imaging is another type of test that measures the temperature of a patient’s skin, revealing metabolic blood flow, which can be elevated where tumor cells are rapidly dividing. Learn more.
Annual Check ups
Annual checkups are essential for maintaining breast health and detecting any changes early. While most findings are benign, early detection of breast cancer offers the most favorable outcomes. Regular screenings and prompt evaluation of any abnormalities ensure that women receive the most appropriate care and support for their breast health needs.
Breast Cancer Screening Methods and Myths Webinar
Watch our breast cancer doctors at the Margie Petersen Breast Center at Providence Saint John’s, discuss the different types of breast cancer screening methods including breast exams, mammography, ultrasounds, MRI, and biopsy, as well as share the facts for all the common breast cancer myths you’ve heard.
Janie Grumley, MD, FACS, Breast Surgical Oncologist and Director, Comprehensive Breast Program, Margie Petersen Breast Center provides a comprehensive overview of the issues and concerns patients may have.
Contact us today to learn more. Patients are often seen the same day and without a requiring a referral.
Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Evaluation
What is a normal mammogram result?
A normal mammogram result indicates no signs of breast cancer. During the screening, radiologist examine the breast images for any abnormalities. If the mammogram is normal:
Normal Results Indicators:
- Breast tissue appears typical.
- No masses, lumps, or suspicious areas are detected.
- No microcalcifications, which could suggest cancer, are present.
Receiving a normal result is reassuring, but regular screenings remain crucial for ongoing breast health. While normal results are positive, continuing with routine mammograms as recommended by your healthcare provider ensures early detection of any future changes. Additionally, report any new breast changes or symptoms to your doctor immediately. Early detection is key in effectively managing breast cancer.
What is the difference between a mammogram and a diagnostic breast exam?
A mammogram and a diagnostic breast exam serve different purposes in breast cancer detection and screening.
Mammogram:
- A mammogram is a routine screening tool.
- It uses low-dose X-rays to capture images of the breast.
- Typically, recommended for women over 40, it helps detect early signs of breast cancer before symptoms appear.
- Regular mammograms can identify tumors that are too small to feel.
Diagnostic Breast Exam
- A diagnostic breast exam follows an abnormal mammogram or noticeable symptoms like a lump.
- This exam involves more detailed imaging techniques, such as additional mammogram vies or ultrasound.
- It focuses on a specific area of concern to determine the cause of the abnormalities.
- Sometimes, a biopsy may be performed if further investigation is needed.
Both procedures are crucial in the fight against breast cancer. While mammograms are preventative, diagnostic breast exams address specific issues, ensuring comprehensive breast health care. Regular screening and prompt diagnostic exams improve early detection and successful treatment outcomes.
How do I prepare for a diagnostic mammogram?
To prepare for a diagnostic mammogram, follow these steps to ensure the best results and a smooth experience.
Before the Exam:
- Schedule your mammogram for a time when your breasts are least likely to be tender, usually a week after your period.
- Avoid using deodorant, perfume, or lotion on your breasts and underarms on the day of the exam, as these can interfere with the images.
During the Exam:
- Wear a two-piece outfit so you only need to remove your top.
- Inform the technician if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Additional Tips:
- Bring previous mammogram images for comparisons.
- Discuss any breast symptoms or concerns with the technician before starting.
- Plan to arrive early to complete any necessary paperwork.
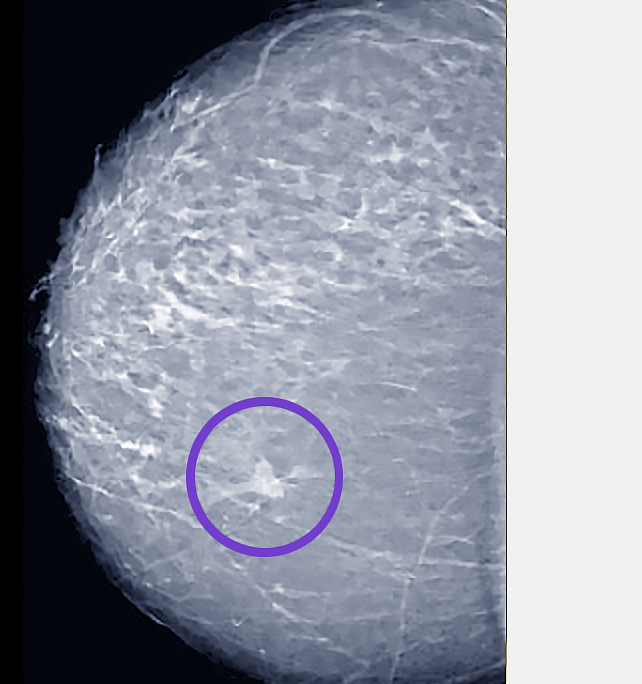
What are suspicious findings in a mammogram?
Suspicious findings on a mammogram require further evaluation to rule out breast cancer. These findings include:
Suspicious Indicators:
- Masses or lumps with irregular shapes or margins, which may suggest cancer.
- Microcalcifications, or tiny calcium deposits, clustered in a specific area, indicating potential malignancy.
- Asymmetry where one breast shows areas that differ significantly from the other.
- Architectural distortion, where the normal structure of breast tissue appears altered.
If any of these signs are present, your radiologist will likely recommend additional imaging, such as an ultrasound or MRI, and possibly a biopsy to determine the nature of the findings.
It’s important to remember that not all suspicious results indicate cancer, but they do warrant further investigation to ensure your breast health. Early detection through careful screening increases the chances of successful treatment, so follow up promptly if you receive such a report.
How common is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women in the United States. It ranks as the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in women, with only lung cancer resulting in more fatalities each year. In 2023, an estimated 297,790 new cases of invasive breast cancer were expected to be diagnosed in U.S. women, along with 55,720 new cases of ductal carcinoma.
How common are diagnostic mammograms?
Regarding mammogram screenings, about 10% of women who have a screening mammogram will be called back for additional imaging, and of those, only about 0.5% to 1% will need a biopsy. The need for a follow-up mammogram or additional imaging often arises from suspicious findings, which could include masses, calcifications, or areas of asymmetry.
Biopsies are performed to confirm the presence of cancer when suspicious findings are detected. Although the majority of these biopsies will not result in a cancer diagnosis, they are essential for ensuring accurate and early detection.
Contact the Margie Petersen Breast Center
The Margie Petersen Breast Center at Providence Saint John’s Health Center is widely renown for its outstanding and compassionate patient care, expert surgical and medical team, and ability to fully evaluate any breast condition in one day.
Meet Our Breast Health Experts
The Breast Health Clinic can be reached at (310) 582-7209. If you have questions regarding a new symptom or want to make an appointment for evaluation please call and a staff member will assist with navigating you in the right direction.